“Having tasted beauty at the heart of the world, we hunger for more.” These are words from Nobel physicist Frank Wilczek in his book, A Beautiful Question. It’s a winsome, joyful meditation on the question: Do cosmic realities embody beautiful ideas? — probing the world, by way of science, as a work of art. He reminds us that time and space, mystery and order, are so much stranger and more generous than we can comprehend. He’s now written a wonderful new book, Fundamentals: Ten Keys to Reality.
Physics, Astronomy & Math
Featured Items
November 21, 2019
Marilynne Robinson and Marcelo Gleiser
The Mystery We Are
Novelist Marilynne Robinson and physicist Marcelo Gleiser are both passionate about the majesty of science, and they share a caution about what they call our modern “piety” toward science. They connect thrilling dots among the current discoveries about the cosmos and the new territory of understanding our own minds. We brought them together for a joyous, heady discussion of the mystery we are.
View
- List View
- Standard View
- Grid View
26 Results
Filters
October 26, 2023
Latanya Sweeney
On Shaping Technology to Human Purpose
You may not know Latanya Sweeney’s name, but as much as any other single person — and with good humor and grace as well as brilliance — she has led on the frontier of our gradual understanding of how far from anonymous you and I are in almost any database we inhabit, and how far from neutral all the algorithms by which we increasingly navigate our lives.
In this conversation with Krista, she brings a helpful big-picture view to our lives with technology, seeing how far we’ve come — and not — since the advent of the internet, and setting that in the context of history both industrial and digital. She insists that we don’t have to accept the harms of digital technology in order to reap its benefits — and she sees very clearly the work that will take. From where she sits, the new generative AI is in equal measure an exciting and alarming evolution. And she shares with us the questions she is asking, and how she and her students and the emerging field of Public Interest Technology might help us all make sense.
This is the second in what will be an ongoing occasional On Being episode to delve into and accompany our lives with this new technological revolution — training clear eyes on downsides and dangers while cultivating an attention to how we might elevate the new frontier of AI — and how, in fact, it might invite us more deeply into our humanity.
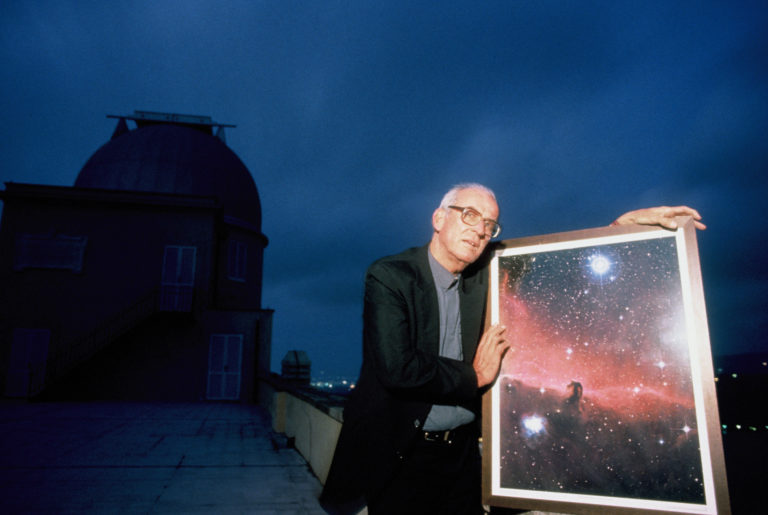
The astrophysicist Mario Livio spent 24 years at the Space Telescope Science Institute working with the Hubble Telescope, which has revealed the reality and beauty of the Universe to scientists and citizens in whole new ways. The Hubble’s successor, the James Webb Telescope, will become fully operational in 2022, and will further some of the questions about the early formation of the Universe and the origins of life to which Mario Livio has been devoted. Krista spoke with him in 2010, and this conversation has become an On Being Classic, imparting a thrilling sense of all we are learning about the cosmos in this generation in time, our terrible earthly woes notwithstanding. Also: how scientific advance always meets recurrent mystery, from the emergence of life in the Universe to the very heart of mathematics and the puzzle of dark matter and dark energy.
If we didn’t have vast civilizational challenges upon us, we might be living in a constant state of wonder at what science in this century is learning and showing us about the cosmos and about ourselves — the new questions it’s giving us to live. We are the generation of our species to map the genome, to detect black holes colliding, to hear gravitational waves. The physicist Brian Greene is one of our greatest interpreters from the human enterprise that is science. And in his most recent thinking and writing, there’s a stunning evolution in his own approach to science and life and the matters of purpose and meaning. We delve into his exuberant, cosmic lens on living in the here and the now.
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence — or SETI — goes beyond hunting for E.T. and habitable planets. Scientists in the field are using telescopes and satellites looking for signs of outright civilizational intelligence. One of the founding pioneers in this search is astronomer Jill Tarter. She is a co-founder of the SETI Institute and was an inspiration for Jodie Foster’s character in the movie Contact, based on the novel by Carl Sagan. To speak with Tarter is to begin to grasp the creative majesty of SETI and what’s relevant now in the ancient question: “Are we alone in the universe?”
“Having tasted beauty at the heart of the world, we hunger for more.” These are words from Nobel physicist Frank Wilczek in his book, A Beautiful Question. It’s a winsome, joyful meditation on the question: Do cosmic realities embody beautiful ideas? — probing the world, by way of science, as a work of art. He reminds us that time and space, mystery and order, are so much stranger and more generous than we can comprehend. He’s now written a wonderful new book, Fundamentals: Ten Keys to Reality.
Physicist Carlo Rovelli says humans don’t understand the world as made by things, “we understand the world made by kisses, or things like kisses — happenings.” This everyday truth is as scientific as it is philosophical and political, and it unfolds with unexpected nuance in his science. Rovelli is one of the founders of loop quantum gravity theory and author of the tiny, bestselling book Seven Brief Lessons on Physics and The Order of Time. Seeing the world through his eyes, we understand that there is no such thing as “here” or “now.” Instead, he says, our senses convey a picture of reality that narrows our understanding of its fullness.
February 20, 2020
George Coyne and Guy Consolmagno
Asteroids, Stars, and the Love of God
The wise and beloved Vatican astronomer Father George Coyne died last week. Like most of the Vatican astronomers across history, he was also a Jesuit. More than 30 objects on the moon are named after the Jesuits who mapped it and ten Jesuits in history have had asteroids named after them. Father Coyne was one of the few with this distinction, alongside his friend and fellow Vatican astronomer Brother Guy Consolmagno. In a conversation filled with laughter, we experience the spacious way the two of them approached life, faith, and the universe.
November 21, 2019
Marilynne Robinson and Marcelo Gleiser
The Mystery We Are
Novelist Marilynne Robinson and physicist Marcelo Gleiser are both passionate about the majesty of science, and they share a caution about what they call our modern “piety” toward science. They connect thrilling dots among the current discoveries about the cosmos and the new territory of understanding our own minds. We brought them together for a joyous, heady discussion of the mystery we are.
Astronomer Natalie Batalha embodies a planetary sense of what “love” is and means. She says her experience searching the universe for exoplanets — earth-like bodies beyond our solar system that could harbor liquid water and life — fundamentally shifted how she thinks about the human experience on this planet. “You see the expanse of the cosmos, and you realize how small we are and how connected we are,” she says. “And that what’s good for you has to be good for me.”
September 28, 2017
Lisa Randall
Dark Matter, Dinosaurs, and Extra Dimensions
“When it comes to the world around us,” Lisa Randall has written, “is there any choice but to explore?” As one of the most influential theoretical physicists working today, she’s interested in the interconnectedness between fields that have previously operated more autonomously: astronomy, biology, and paleontology. She’s pursuing a theory that “dark matter” might have created the cosmic event that led to the extinction of the dinosaurs — and hence humanity’s rise as a species. We learn what she’s discovering, as well as the human questions and takeaways her work throws into relief.
A philosopher’s questioning and a scientist’s eye shape Enrique Martínez Celaya’s original approach to art and to life. A world-renowned painter who trained as a physicist, he’s fascinated by the deeper order that “whispers” beneath the surface of things. Works of art that endure, he says, possess their own form of consciousness. And a quiet life of purpose is a particular form of prophecy.
A thrilling, mind-bending view of the cosmos and of the human adventure of modern science. In a conversation ranging from free will to the multiverse to the meaning of the Higgs boson particle, physicist Brian Greene suggests the deepest scientific realities are hidden from human senses and often defy our best intuition.
A passionate translator of the beauty and relevance of scientific questions, Margaret Wertheim is also wise about the limits of science to tell the whole story of the human self. Her Institute for Figuring in Los Angeles reveals evocative, visceral connections between high mathematics, crochet and other folk arts, and our love of for the planet.
Fundamental forces of physics somehow determine everything that happens, “from the birth of a child to the birth of a galaxy.” Yet physicist Leonard Mlodinow has an intriguing perspective on the gap between theory and reality — and the fascinating interplay between a life in science and life in the world. As the child of two Holocaust survivors, he asks questions about our capacity to create our lives, while reflecting on extreme human cruelty — and courage.
An astrophysicist who studies the shape of the universe, Janna Levin has also explored her science by writing a novel about two pivotal 20th-century mathematicians, Kurt Gödel and Alan Turing. Both men pushed at boundaries where mathematics presses on grand questions of meaning and purpose. Such questions, she says, help create the technologies that are now changing our sense of what it means to be human.
Parallel realities and the deep structure of space-time sound like science fiction. These are matters of real scientific inquiry. Lord Martin Rees is an astrophysicist and self-professed atheist who paints a fascinating picture of how we might be changed by what we do not yet know.
September 19, 2013
Keith Devlin
The Joy of Math: Learning and What It Means To Be Human
Mathematical equations are like sonnets says Keith Devlin. What most of us learn in school, he says, doesn’t begin to convey what mathematics is. And technology may free more of us to discover the wonder of mathematical thinking — as a reflection of the inner world of our minds.
What happens when you bring together science and poetry on something like color or light? Arthur Zajonc is a physicist and contemplative. And he says we can all investigate life as vigorously from the inside as from the outside.
The Pause
Join our constellation of listening and living.
The Pause is a monthly Saturday morning companion to all things On Being, with heads-up on new episodes, special offerings, event invitations, recommendations, and reflections from Krista all year round.
Search results for “”
View
- List View
- Standard View
- Grid View
Filters